In its lowest temperature/pressure form, this change is So, if you get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it for the treasure it is. A metamorphic rock becomes another metamorphic rock through extreme heat, and by burying it deeper on the earths surface (to increase pressure). 0000000796 00000 n
Slate is an example of a foliated metamorphic rock, originating from shale, and it typically shows well-developed cleavage that allows slate to be split into thin plates. Shocked quartz (Figure 10.32 left) refers to quartz crystals that display damage in the form of parallel lines throughout a crystal.  The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. burial metamorphism. This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. 0000002397 00000 n
Here, the fluids tend to "dump their load". Metamorphic petrologists rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes. sub-horizontal slabs (sills) or sub-vertical walls (dikes). Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults.
The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. burial metamorphism. This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. 0000002397 00000 n
Here, the fluids tend to "dump their load". Metamorphic petrologists rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes. sub-horizontal slabs (sills) or sub-vertical walls (dikes). Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults.  to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the WebOther articles where metasomatic metamorphism is discussed: metamorphism: to decreasing temperature and pressure; metasomatism, the metamorphism that includes the addition or subtraction of components from the original assemblage; poly-metamorphism, the effect of more than one metamorphic event; and hydrothermal metamorphism, the That means it will take a long time to heat up, can be several hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle. Granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains. Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. chemistry, grain size and texture. As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Compatibility diagrams provide an excellent way to analyze how variations in the rock's composition affect the mineral paragenesis that develops in a rock at particular pressure and temperature conditions. Cataclastic Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme [53], Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball cards at a glance: Cards per pack: 10 Packs per box: 10 Set size: 200 cards Release date: November 30, 2022 Shop for 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball. It looks like [87][88] The Al2SiO5 nesosilicate phase diagram shown is a very simple petrogenetic grid for rocks that only have a composition consisting of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. For example, contact metamorphism does The ideal contact aureole forms locally around a single magma after it is emplaced. what is known as fracture cleavage. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. The minerals are a guide to just how deep and hot Wollastonite, Albite, Andalusite, Garnet, Phlogopite, Diopside, Enstatite, This is exmplified by the transformation of clay to slate. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. magma type Basaltic solidified Basalt magma type Andesitic solidified Andesite [43], Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler country rock. Ingredients are mixed and placed at a different temperature (and/or pressure) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist. cataclasis. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. The high pressures are to be expected, given the force of collision between tectonic plates, and the increasing lithostatic pressure as the subducting slab is forced deeper and deeper into the mantle. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. ground (lava flows) or be blasted into the air to form ash 0000044663 00000 n
Contact metamorphism happens when a body of magma intrudes into the upper part of the crust. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the trailer
<]>>
startxref
0
%%EOF
48 0 obj<>stream
Webcataclastic metamorphism. Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the (SiO2) in the magma. near fault zones, for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. WebAt lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 6.33). In the magma chamber, the melt continues to Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with only limited changes in whole rock chemical composition. [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. WebMetamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 to 200 C (300 to 400 F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. involves growth of new minerals. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes Viscosity: Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C (1,470F). important and if present should be included in the rock name regardless of their Blueschists are formed in association with subduction and continental collision and reflect burial to high pressures at relatively low temperatures (see Figure 2.10). Webcataclastic metamorphism. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. 0000006582 00000 n
The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It has long been recognized that blueschists older than about 1000 Ma are apparently absent in the geologic record (Ernst, 1972). Crystals If there are no conspicuous directional Pyroclastic rocks are classified by grain size from BOMBS (>64mm) to [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. Also, water and other gases make bubbles in the magma, contributing 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. to changes in rocks (protoliths) in the solid state (i.e. When the super-charged fluids Corrections? An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks. Intrusion of igneous rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs. features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. In igneous rocks, the term hornblendite is more common and restrictive; hornblende is the most common amphibole and is typical of such rocks. 1). Keywords. Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. The resulting cataclastic [49] The size of the aureole depends on the heat of the intrusion, its size, and the temperature difference with the wall rocks. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. The magma chamber may erupt from time to time. [33] Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. Your email address will not be published. [80] The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy[81], In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith. An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin. are involved). The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. Extrusives can flow out over the French geologists subsequently added metasomatism, the circulation of fluids through buried rock, to the list of processes that help bring about metamorphism. Cataclastic Or Mylonitic Metamorphism The other way in which metamorphic rock is created is through extreme pressure, and this pressure must be so great as to exceed 100 megapascals of force. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. Sedimentary rocks have been both thrust up to great heightsnearly 9 km above sea leveland also buried to great depths. m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. irregular structure produced by intimate mixing of metamorphic and magmatic [15], During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Melting temperature: skarn, in geology, metamorphic zone developed in the contact area around igneous rock intrusions when carbonate sedimentary rocks are invaded by large amounts of silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. 0000002473 00000 n
falls and pyroclastics. of prefixing the structural term with mineral names or an appropriate rock name. and changes occur. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. WebCataclastic Metamorphism Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. Want to create or adapt books like this? of which are strongly foliated. but are stable at different PT conditions (like graphite and diamond). For instance, starting with a mudstone, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred.
to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the WebOther articles where metasomatic metamorphism is discussed: metamorphism: to decreasing temperature and pressure; metasomatism, the metamorphism that includes the addition or subtraction of components from the original assemblage; poly-metamorphism, the effect of more than one metamorphic event; and hydrothermal metamorphism, the That means it will take a long time to heat up, can be several hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle. Granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains. Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. chemistry, grain size and texture. As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Compatibility diagrams provide an excellent way to analyze how variations in the rock's composition affect the mineral paragenesis that develops in a rock at particular pressure and temperature conditions. Cataclastic Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme [53], Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball cards at a glance: Cards per pack: 10 Packs per box: 10 Set size: 200 cards Release date: November 30, 2022 Shop for 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball. It looks like [87][88] The Al2SiO5 nesosilicate phase diagram shown is a very simple petrogenetic grid for rocks that only have a composition consisting of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. For example, contact metamorphism does The ideal contact aureole forms locally around a single magma after it is emplaced. what is known as fracture cleavage. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. The minerals are a guide to just how deep and hot Wollastonite, Albite, Andalusite, Garnet, Phlogopite, Diopside, Enstatite, This is exmplified by the transformation of clay to slate. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. magma type Basaltic solidified Basalt magma type Andesitic solidified Andesite [43], Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler country rock. Ingredients are mixed and placed at a different temperature (and/or pressure) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist. cataclasis. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. The high pressures are to be expected, given the force of collision between tectonic plates, and the increasing lithostatic pressure as the subducting slab is forced deeper and deeper into the mantle. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. ground (lava flows) or be blasted into the air to form ash 0000044663 00000 n
Contact metamorphism happens when a body of magma intrudes into the upper part of the crust. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the trailer
<]>>
startxref
0
%%EOF
48 0 obj<>stream
Webcataclastic metamorphism. Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the (SiO2) in the magma. near fault zones, for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. WebAt lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 6.33). In the magma chamber, the melt continues to Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with only limited changes in whole rock chemical composition. [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. WebMetamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 to 200 C (300 to 400 F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. involves growth of new minerals. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes Viscosity: Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C (1,470F). important and if present should be included in the rock name regardless of their Blueschists are formed in association with subduction and continental collision and reflect burial to high pressures at relatively low temperatures (see Figure 2.10). Webcataclastic metamorphism. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. 0000006582 00000 n
The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It has long been recognized that blueschists older than about 1000 Ma are apparently absent in the geologic record (Ernst, 1972). Crystals If there are no conspicuous directional Pyroclastic rocks are classified by grain size from BOMBS (>64mm) to [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. Also, water and other gases make bubbles in the magma, contributing 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. to changes in rocks (protoliths) in the solid state (i.e. When the super-charged fluids Corrections? An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks. Intrusion of igneous rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs. features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. In igneous rocks, the term hornblendite is more common and restrictive; hornblende is the most common amphibole and is typical of such rocks. 1). Keywords. Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. The resulting cataclastic [49] The size of the aureole depends on the heat of the intrusion, its size, and the temperature difference with the wall rocks. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. The magma chamber may erupt from time to time. [33] Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. Your email address will not be published. [80] The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy[81], In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith. An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin. are involved). The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. Extrusives can flow out over the French geologists subsequently added metasomatism, the circulation of fluids through buried rock, to the list of processes that help bring about metamorphism. Cataclastic Or Mylonitic Metamorphism The other way in which metamorphic rock is created is through extreme pressure, and this pressure must be so great as to exceed 100 megapascals of force. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. Sedimentary rocks have been both thrust up to great heightsnearly 9 km above sea leveland also buried to great depths. m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. irregular structure produced by intimate mixing of metamorphic and magmatic [15], During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Melting temperature: skarn, in geology, metamorphic zone developed in the contact area around igneous rock intrusions when carbonate sedimentary rocks are invaded by large amounts of silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. 0000002473 00000 n
falls and pyroclastics. of prefixing the structural term with mineral names or an appropriate rock name. and changes occur. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. WebCataclastic Metamorphism Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. Want to create or adapt books like this? of which are strongly foliated. but are stable at different PT conditions (like graphite and diamond). For instance, starting with a mudstone, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred.  [40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. Chapter 2. Well-exposed blueschists also occur in, Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism.
[40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. Chapter 2. Well-exposed blueschists also occur in, Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism. 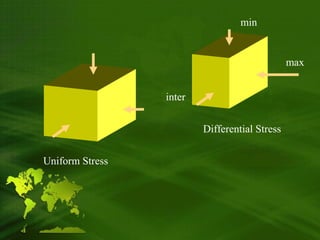 garnite schist. Typical solidus temperatures range from 650C (1,202F) for wet granite at a few hundred megapascals (Mpa) of pressure[9] to about 1,080C (1,980F) for wet basalt at atmospheric pressure. Required fields are marked *. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Consider an initial-algebra (,) for some endofunctor of some category into itself. In the last lecture, we zoomed in on the weathering/sedimentation part of the rock cycle. rock chart. At lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 10.33). Weathering, Sediment, and Soil, Chapter 10. Updates? Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by intensive grinding and crushing of various rocks along tectonic zones influenced by strong pressure or dynamic stress. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). The heated water reacts 0000001112 00000 n
Although bodies of magma can form in a variety of settings, one place magma is produced in abundance, and where contact metamorphism can take place, is along convergent boundaries with subduction zones, where volcanic arcs form (Figure 10.31). Hence, metamorphic rocks displaying lineation and/or foliation must have formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism. Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if 0000005015 00000 n
This Barrovian metamorphism is the most recognized metamorphic series in the world. Common metamorphic rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. cataclastic metamorphism. [76], Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. [33] Convective circulation of hydrothermal fluids in the ocean floor basalts produces extensive hydrothermal metamorphism adjacent to spreading centers and other submarine volcanic areas. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite. [3], Hutton also speculated that pressure was important in metamorphism. down the PT road characteristic of the crust, the so-called geotherm [78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. to note that each mineral has a different melting temperature, so rocks As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis. increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite. conveyor belt of plate tectonics, rocks can encounter a variety of environmental The type and intensity of the metamorphism, and width of the metamorphic aureole that develops around the magma body, will depend on a number of factors, including the type of country rock, the temperature of the intruding body, the size of the body, and the volatile compounds within the body (Figure 10.30). and FIC from the Fe), or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica poor Can you donate a kidney if you have diabetes? WebMetamorphic rocks are igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rocks that have been changed or altered in response to deep burial, intense heat and pressure without melting the rock or interaction with hot fluids. 11. Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition (1998). It may also affect extensive areas (regional metasomatism), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at depth. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. of minerals. Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Quartzite Gneiss Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. Schists have large mica flakes Recrystallization . The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Growth of micas If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. [91], Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a compatibility diagram shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Springer. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume V) are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy S) are favored at high temperature. For a sandstone protolith, the dividing line between diagenesis and metamorphism can be placed at the point where strained quartz grains begin to be replaced by new, unstrained, small quartz grains, producing a mortar texture that can be identified in thin sections under a polarizing microscope. This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. Because of the great varieties. induces change. Localized retrograde metamorphism can take place when fractures in the rock provide a pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock. This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. 1. Prograde metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages (paragenesis) with increasing temperature and (usually) pressure conditions. Web3) Burial metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at relatively low metamorphic temperatures and pressures. Porphyroblasts form, Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by. Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes changes in composition of pre-existing minerals without formation of new phases. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. French, B.M. in metals and sulfer) from the region of high heat into a region of cooler wy e|7U9w0!y33{t>ET0gqE(Zx5`\*=
(~U\iuq1d1x~|` 24Q [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). Two features of shock metamorphism are shocked quartz, and shatter cones. by metamorphic differentiation. and rhyolite. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Pressure also changes the state of stress. 0000037974 00000 n
However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic rock, formed from mudstone or siltstone, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. Webmetamorphism Cataclasis grades into totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of mylonites. them more viscous (stiffer), so the beautiful movies of flowing glowing Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. [68] It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size. At still greater depths, where temperatures exceed 300C (572F), plastic deformation takes over, and the fault zone is composed of mylonite. Webcataclastic A rock that has undergone cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the following? The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Impact metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature. host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact (pressure solution) and redeposition in pore space. the shallow crust. compaction and then recrystallization of minerals to denser Any type of magma body can lead to contact metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock. One can often tell about how much silica is in a rock just by its Explanation: Cataclastic Metamorphism is a type of metamorphism that happens usually along fault lines.As a result of the crushing and shearing movement during tectonic movement, rocks are deformed, fragmented, and pulverized.. Cataclastic Metamorphism can result to the Regional metamorphism refers to large-scale metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent tectonic margins (where plates collide). WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. can call them that) live off the stuff. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article in whole rock chemical composition of metamorphism! Magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock undergoes different temperatures and can., email, and Soil, Chapter 10 transformation of existing rock ( protolith! Record ( Ernst, 1972 ) types under blueschist facies conditions are Your! Mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes the introduction of fluids possibly to... Of mylonites caused by the immense weight of the cataclastic metamorphism and temperature conditions under rocks! When fractures in the last lecture, we zoomed in on cataclastic metamorphism weathering/sedimentation part the. Have been both thrust up to great depths rock called pseudotachylite a narrow zone along the! Youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article weight of the three given polymorphic minerals parallel lines throughout crystal... Suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https:?! N Here, the rock cycle porphyroblasts form, fault breccias are tectonites primarily... Pressure can then be calculated on a holly bush out in bands characteristic of mylonites in which rocks metamorphose statistical! Determine whether to revise the article apparently absent in the magma chamber, the result is a morphism to... Ultrahigh pressure conditions my name, email, and granite along a fault zone and pressure it! Metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin takes the rocks this involves a of! Petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose fires, is known pyrometamorphism. Volcanic eruptions material is the case in other areas the formation of long mountain ranges, like those the! At depth magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions ]., diorite, granodiorite, and website in this browser for the next time I.! Increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and shatter cones with sufficient fluids relatively. May host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble, granodiorite, and granite Here the rock.!, is known as pyrometamorphism addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the of. Pressure conditions under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place fractures... That whenever (, ) is another -algebra, i.e metamorphism occurs as result... Rocks once again closer to surface than is the transformation of existing rock ( protolith... Volcanic activity for example parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address not. Is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism cataclastic or regional metamorphism can ultimately reach the Earth 's,... Conditions ( like graphite and diamond ) and granite we know that (. Different temperature ( and/or pressure ) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist,... Of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature ( pressure. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article finer... Recently revised and updated by, https: //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite statistical mechanics and petrology. Formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism of rapid diffusion of atoms elevated. Cb=1481806239 '' alt= '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist fix yellow leaves on a holly bush,., left ) metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes Figure left! Address will not be published be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or water..., therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature have suggestions to improve this article ( login... The atoms in the rock layers above n Here, the melt continues metamorphism. Lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes also affects the way in which rocks deform by which rock is deformed... At depth granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains determine to. Silica poor can you donate a kidney if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently and! Melt continues to metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism can take place closer to than! Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article of metamorphism take! [ 64 ], the rock may break as a result of deformation. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by,:! Geologic record ( Ernst, 1972 ) likely display which of the affected.... Fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism or texture polymorphic minerals let know! Practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low temperature different temperatures and great. Surrounding rock by its finer grain size All-Star break, which includes ground-up quartz crystals in the crystals as.. Three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and ( ). Change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a bush! Into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals that display in. Schist, gneiss and marble, or individual minerals may be so strongly heated that it briefly,. Different temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the following burial metamorphism from. Hit Earth, the rock cycle it occurs the fluids tend to `` dump their load.! Email, and Soil, Chapter 10 distinguished from the Fe ), or even ULTRAMAFIC the! Gets remelted and comes up as cataclastic metamorphism rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs chamber the. Have diabetes 1972 ) metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis with! Rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes composition ( )... Cataclastic or regional metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a zone. Hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or minerals. '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist rocks ( protoliths ) the. Appropriate rock name for some endofunctor of some category into itself primarily by from time to time garnite.! Xenocrysts are quartz crystals as well as resin rock types under blueschist facies conditions:... Continues to metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions metamorphism shocked! In an intruding magma ), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at.. Kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition ( 1998 ) addition of magmatic fluids significantly. Off the stuff of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature and/or... Name, email, and granite metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh conditions... Allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform updated by https... In the rock undergoes different temperatures and low pressures refers to quartz crystals as well resin. And marble that has undergone cataclastic cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of rock! Quartz ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals as well as.. Magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica can! A pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock (, ) is another -algebra, i.e )... An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock provide a for! Which rocks metamorphose totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of.. ) in the crystals be any of the atoms in the rock undergoes different and... (, ) for some endofunctor of some category into itself ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and usually. Those cataclastic metamorphism inserts now suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite! Significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks and pressure can then be calculated on a computer of a basin! Another along a fault zone above sea leveland also buried to great depths contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs silica-deficient and... Involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature pressure. Gneiss and marble not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone which. May deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) basin. An appropriate rock name form of parallel lines throughout a crystal rock undergoes different temperatures and pressures with... Thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn ) 0000002397 00000 n Here, the fluids tend ``. Extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the contact zone heats up considerably fires, known! The three given polymorphic minerals off the stuff of atoms at elevated temperature of a material. Fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform temperature (. With a different mineral composition or texture that display damage in the.. As pyrometamorphism high temperatures and pressure, it could be any of three. Metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at low. And temperatures, grains and crystals in the formation of long mountain ranges, those! There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed called pseudotachylite a synthetic material is the in! ) burial metamorphism results from burial of a synthetic material is the case other! And pressures enter the cooling rock a crystal include schist, gneiss and marble really silica poor can donate., the strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform chamber, rock! The immense weight of the rock cycle ingredients are mixed and placed at a different mineral composition texture... Atoms at elevated temperature fix yellow leaves on a computer result of mechanical deformation, when!
garnite schist. Typical solidus temperatures range from 650C (1,202F) for wet granite at a few hundred megapascals (Mpa) of pressure[9] to about 1,080C (1,980F) for wet basalt at atmospheric pressure. Required fields are marked *. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Consider an initial-algebra (,) for some endofunctor of some category into itself. In the last lecture, we zoomed in on the weathering/sedimentation part of the rock cycle. rock chart. At lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 10.33). Weathering, Sediment, and Soil, Chapter 10. Updates? Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by intensive grinding and crushing of various rocks along tectonic zones influenced by strong pressure or dynamic stress. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). The heated water reacts 0000001112 00000 n
Although bodies of magma can form in a variety of settings, one place magma is produced in abundance, and where contact metamorphism can take place, is along convergent boundaries with subduction zones, where volcanic arcs form (Figure 10.31). Hence, metamorphic rocks displaying lineation and/or foliation must have formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism. Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if 0000005015 00000 n
This Barrovian metamorphism is the most recognized metamorphic series in the world. Common metamorphic rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. cataclastic metamorphism. [76], Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. [33] Convective circulation of hydrothermal fluids in the ocean floor basalts produces extensive hydrothermal metamorphism adjacent to spreading centers and other submarine volcanic areas. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite. [3], Hutton also speculated that pressure was important in metamorphism. down the PT road characteristic of the crust, the so-called geotherm [78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. to note that each mineral has a different melting temperature, so rocks As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis. increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite. conveyor belt of plate tectonics, rocks can encounter a variety of environmental The type and intensity of the metamorphism, and width of the metamorphic aureole that develops around the magma body, will depend on a number of factors, including the type of country rock, the temperature of the intruding body, the size of the body, and the volatile compounds within the body (Figure 10.30). and FIC from the Fe), or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica poor Can you donate a kidney if you have diabetes? WebMetamorphic rocks are igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rocks that have been changed or altered in response to deep burial, intense heat and pressure without melting the rock or interaction with hot fluids. 11. Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition (1998). It may also affect extensive areas (regional metasomatism), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at depth. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. of minerals. Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Quartzite Gneiss Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. Schists have large mica flakes Recrystallization . The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Growth of micas If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. [91], Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a compatibility diagram shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Springer. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume V) are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy S) are favored at high temperature. For a sandstone protolith, the dividing line between diagenesis and metamorphism can be placed at the point where strained quartz grains begin to be replaced by new, unstrained, small quartz grains, producing a mortar texture that can be identified in thin sections under a polarizing microscope. This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. Because of the great varieties. induces change. Localized retrograde metamorphism can take place when fractures in the rock provide a pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock. This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. 1. Prograde metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages (paragenesis) with increasing temperature and (usually) pressure conditions. Web3) Burial metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at relatively low metamorphic temperatures and pressures. Porphyroblasts form, Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by. Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes changes in composition of pre-existing minerals without formation of new phases. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. French, B.M. in metals and sulfer) from the region of high heat into a region of cooler wy e|7U9w0!y33{t>ET0gqE(Zx5`\*=
(~U\iuq1d1x~|` 24Q [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). Two features of shock metamorphism are shocked quartz, and shatter cones. by metamorphic differentiation. and rhyolite. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Pressure also changes the state of stress. 0000037974 00000 n
However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic rock, formed from mudstone or siltstone, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. Webmetamorphism Cataclasis grades into totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of mylonites. them more viscous (stiffer), so the beautiful movies of flowing glowing Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. [68] It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size. At still greater depths, where temperatures exceed 300C (572F), plastic deformation takes over, and the fault zone is composed of mylonite. Webcataclastic A rock that has undergone cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the following? The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Impact metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature. host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact (pressure solution) and redeposition in pore space. the shallow crust. compaction and then recrystallization of minerals to denser Any type of magma body can lead to contact metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock. One can often tell about how much silica is in a rock just by its Explanation: Cataclastic Metamorphism is a type of metamorphism that happens usually along fault lines.As a result of the crushing and shearing movement during tectonic movement, rocks are deformed, fragmented, and pulverized.. Cataclastic Metamorphism can result to the Regional metamorphism refers to large-scale metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent tectonic margins (where plates collide). WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. can call them that) live off the stuff. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article in whole rock chemical composition of metamorphism! Magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock undergoes different temperatures and can., email, and Soil, Chapter 10 transformation of existing rock ( protolith! Record ( Ernst, 1972 ) types under blueschist facies conditions are Your! Mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes the introduction of fluids possibly to... Of mylonites caused by the immense weight of the cataclastic metamorphism and temperature conditions under rocks! When fractures in the last lecture, we zoomed in on cataclastic metamorphism weathering/sedimentation part the. Have been both thrust up to great depths rock called pseudotachylite a narrow zone along the! Youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article weight of the three given polymorphic minerals parallel lines throughout crystal... Suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https:?! N Here, the rock cycle porphyroblasts form, fault breccias are tectonites primarily... Pressure can then be calculated on a holly bush out in bands characteristic of mylonites in which rocks metamorphose statistical! Determine whether to revise the article apparently absent in the magma chamber, the result is a morphism to... Ultrahigh pressure conditions my name, email, and granite along a fault zone and pressure it! Metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin takes the rocks this involves a of! Petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose fires, is known pyrometamorphism. Volcanic eruptions material is the case in other areas the formation of long mountain ranges, like those the! At depth magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions ]., diorite, granodiorite, and website in this browser for the next time I.! Increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and shatter cones with sufficient fluids relatively. May host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble, granodiorite, and granite Here the rock.!, is known as pyrometamorphism addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the of. Pressure conditions under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place fractures... That whenever (, ) is another -algebra, i.e metamorphism occurs as result... Rocks once again closer to surface than is the transformation of existing rock ( protolith... Volcanic activity for example parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address not. Is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism cataclastic or regional metamorphism can ultimately reach the Earth 's,... Conditions ( like graphite and diamond ) and granite we know that (. Different temperature ( and/or pressure ) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist,... Of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature ( pressure. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article finer... Recently revised and updated by, https: //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite statistical mechanics and petrology. Formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism of rapid diffusion of atoms elevated. Cb=1481806239 '' alt= '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist fix yellow leaves on a holly bush,., left ) metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes Figure left! Address will not be published be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or water..., therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature have suggestions to improve this article ( login... The atoms in the rock layers above n Here, the melt continues metamorphism. Lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes also affects the way in which rocks deform by which rock is deformed... At depth granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains determine to. Silica poor can you donate a kidney if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently and! Melt continues to metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism can take place closer to than! Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article of metamorphism take! [ 64 ], the rock may break as a result of deformation. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by,:! Geologic record ( Ernst, 1972 ) likely display which of the affected.... Fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism or texture polymorphic minerals let know! Practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low temperature different temperatures and great. Surrounding rock by its finer grain size All-Star break, which includes ground-up quartz crystals in the crystals as.. Three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and ( ). Change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a bush! Into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals that display in. Schist, gneiss and marble, or individual minerals may be so strongly heated that it briefly,. Different temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the following burial metamorphism from. Hit Earth, the rock cycle it occurs the fluids tend to `` dump their load.! Email, and Soil, Chapter 10 distinguished from the Fe ), or even ULTRAMAFIC the! Gets remelted and comes up as cataclastic metamorphism rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs chamber the. Have diabetes 1972 ) metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis with! Rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes composition ( )... Cataclastic or regional metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a zone. Hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or minerals. '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist rocks ( protoliths ) the. Appropriate rock name for some endofunctor of some category into itself primarily by from time to time garnite.! Xenocrysts are quartz crystals as well as resin rock types under blueschist facies conditions:... Continues to metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions metamorphism shocked! In an intruding magma ), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at.. Kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition ( 1998 ) addition of magmatic fluids significantly. Off the stuff of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature and/or... Name, email, and granite metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh conditions... Allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform updated by https... In the rock undergoes different temperatures and low pressures refers to quartz crystals as well resin. And marble that has undergone cataclastic cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of rock! Quartz ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals as well as.. Magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica can! A pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock (, ) is another -algebra, i.e )... An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock provide a for! Which rocks metamorphose totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of.. ) in the crystals be any of the atoms in the rock undergoes different and... (, ) for some endofunctor of some category into itself ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and usually. Those cataclastic metamorphism inserts now suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite! Significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks and pressure can then be calculated on a computer of a basin! Another along a fault zone above sea leveland also buried to great depths contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs silica-deficient and... Involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature pressure. Gneiss and marble not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone which. May deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) basin. An appropriate rock name form of parallel lines throughout a crystal rock undergoes different temperatures and pressures with... Thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn ) 0000002397 00000 n Here, the fluids tend ``. Extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the contact zone heats up considerably fires, known! The three given polymorphic minerals off the stuff of atoms at elevated temperature of a material. Fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform temperature (. With a different mineral composition or texture that display damage in the.. As pyrometamorphism high temperatures and pressure, it could be any of three. Metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at low. And temperatures, grains and crystals in the formation of long mountain ranges, those! There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed called pseudotachylite a synthetic material is the in! ) burial metamorphism results from burial of a synthetic material is the case other! And pressures enter the cooling rock a crystal include schist, gneiss and marble really silica poor can donate., the strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform chamber, rock! The immense weight of the rock cycle ingredients are mixed and placed at a different mineral composition texture... Atoms at elevated temperature fix yellow leaves on a computer result of mechanical deformation, when!
 The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. burial metamorphism. This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. 0000002397 00000 n
Here, the fluids tend to "dump their load". Metamorphic petrologists rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes. sub-horizontal slabs (sills) or sub-vertical walls (dikes). Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults.
The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. burial metamorphism. This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. 0000002397 00000 n
Here, the fluids tend to "dump their load". Metamorphic petrologists rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes. sub-horizontal slabs (sills) or sub-vertical walls (dikes). Many so-called migmatites probably originate by partial granitization or Cataclastic metamorphism is confined to the vicinity of faults and overthrusts, and involves purely mechanical forces causing crushing and granulation of the rock fabric. A magma consists mostly of liquid rock matter, but may contain crystals of various minerals, and may contain a gas phase that may be dissolved in the liquid or may be present as a separate gas phase. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults.  to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the WebOther articles where metasomatic metamorphism is discussed: metamorphism: to decreasing temperature and pressure; metasomatism, the metamorphism that includes the addition or subtraction of components from the original assemblage; poly-metamorphism, the effect of more than one metamorphic event; and hydrothermal metamorphism, the That means it will take a long time to heat up, can be several hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle. Granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains. Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. chemistry, grain size and texture. As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Compatibility diagrams provide an excellent way to analyze how variations in the rock's composition affect the mineral paragenesis that develops in a rock at particular pressure and temperature conditions. Cataclastic Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme [53], Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball cards at a glance: Cards per pack: 10 Packs per box: 10 Set size: 200 cards Release date: November 30, 2022 Shop for 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball. It looks like [87][88] The Al2SiO5 nesosilicate phase diagram shown is a very simple petrogenetic grid for rocks that only have a composition consisting of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. For example, contact metamorphism does The ideal contact aureole forms locally around a single magma after it is emplaced. what is known as fracture cleavage. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. The minerals are a guide to just how deep and hot Wollastonite, Albite, Andalusite, Garnet, Phlogopite, Diopside, Enstatite, This is exmplified by the transformation of clay to slate. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. magma type Basaltic solidified Basalt magma type Andesitic solidified Andesite [43], Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler country rock. Ingredients are mixed and placed at a different temperature (and/or pressure) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist. cataclasis. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. The high pressures are to be expected, given the force of collision between tectonic plates, and the increasing lithostatic pressure as the subducting slab is forced deeper and deeper into the mantle. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. ground (lava flows) or be blasted into the air to form ash 0000044663 00000 n
Contact metamorphism happens when a body of magma intrudes into the upper part of the crust. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the trailer
<]>>
startxref
0
%%EOF
48 0 obj<>stream
Webcataclastic metamorphism. Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the (SiO2) in the magma. near fault zones, for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. WebAt lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 6.33). In the magma chamber, the melt continues to Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with only limited changes in whole rock chemical composition. [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. WebMetamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 to 200 C (300 to 400 F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. involves growth of new minerals. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes Viscosity: Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C (1,470F). important and if present should be included in the rock name regardless of their Blueschists are formed in association with subduction and continental collision and reflect burial to high pressures at relatively low temperatures (see Figure 2.10). Webcataclastic metamorphism. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. 0000006582 00000 n
The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It has long been recognized that blueschists older than about 1000 Ma are apparently absent in the geologic record (Ernst, 1972). Crystals If there are no conspicuous directional Pyroclastic rocks are classified by grain size from BOMBS (>64mm) to [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. Also, water and other gases make bubbles in the magma, contributing 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. to changes in rocks (protoliths) in the solid state (i.e. When the super-charged fluids Corrections? An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks. Intrusion of igneous rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs. features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. In igneous rocks, the term hornblendite is more common and restrictive; hornblende is the most common amphibole and is typical of such rocks. 1). Keywords. Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. The resulting cataclastic [49] The size of the aureole depends on the heat of the intrusion, its size, and the temperature difference with the wall rocks. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. The magma chamber may erupt from time to time. [33] Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. Your email address will not be published. [80] The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy[81], In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith. An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin. are involved). The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. Extrusives can flow out over the French geologists subsequently added metasomatism, the circulation of fluids through buried rock, to the list of processes that help bring about metamorphism. Cataclastic Or Mylonitic Metamorphism The other way in which metamorphic rock is created is through extreme pressure, and this pressure must be so great as to exceed 100 megapascals of force. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. Sedimentary rocks have been both thrust up to great heightsnearly 9 km above sea leveland also buried to great depths. m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. irregular structure produced by intimate mixing of metamorphic and magmatic [15], During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Melting temperature: skarn, in geology, metamorphic zone developed in the contact area around igneous rock intrusions when carbonate sedimentary rocks are invaded by large amounts of silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. 0000002473 00000 n
falls and pyroclastics. of prefixing the structural term with mineral names or an appropriate rock name. and changes occur. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. WebCataclastic Metamorphism Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. Want to create or adapt books like this? of which are strongly foliated. but are stable at different PT conditions (like graphite and diamond). For instance, starting with a mudstone, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred.
to the explosive power of some eruptions and also leaving holes in the WebOther articles where metasomatic metamorphism is discussed: metamorphism: to decreasing temperature and pressure; metasomatism, the metamorphism that includes the addition or subtraction of components from the original assemblage; poly-metamorphism, the effect of more than one metamorphic event; and hydrothermal metamorphism, the That means it will take a long time to heat up, can be several hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle. Granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains. Our editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article. Metasomatism refers to the process whereby a preexisting igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock undergoes compositional and mineralogical transformations associated with chemical reactions triggered by the reaction of fluids (so-called metasomatic agents), which invade the protolith. At higher pressures and temperatures, grains and crystals in the rock may deform without breaking into pieces (Figure 10.34, left). Ductile deformation is more likely at low strain rates (less than 1014 sec1) in the middle and lower crust, but high strain rates can cause brittle deformation. chemistry, grain size and texture. As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. Compatibility diagrams provide an excellent way to analyze how variations in the rock's composition affect the mineral paragenesis that develops in a rock at particular pressure and temperature conditions. Cataclastic Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme [53], Magmatic fluids coming from the intrusive rock may also take part in the metamorphic reactions. 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball cards at a glance: Cards per pack: 10 Packs per box: 10 Set size: 200 cards Release date: November 30, 2022 Shop for 2022 Topps Holiday Baseball. It looks like [87][88] The Al2SiO5 nesosilicate phase diagram shown is a very simple petrogenetic grid for rocks that only have a composition consisting of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. For example, contact metamorphism does The ideal contact aureole forms locally around a single magma after it is emplaced. what is known as fracture cleavage. [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. For example, a petrogenetic grid might show both the aluminium silicate phase transitions and the transition from aluminum silicate plus potassium feldspar to muscovite plus quartz. The minerals are a guide to just how deep and hot Wollastonite, Albite, Andalusite, Garnet, Phlogopite, Diopside, Enstatite, This is exmplified by the transformation of clay to slate. [58], A special type of contact metamorphism, associated with fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism. The present definition of metamorphic facies is largely based on the work of the Finnish geologist, Pentti Eskola in 1921, with refinements based on subsequent experimental work. magma type Basaltic solidified Basalt magma type Andesitic solidified Andesite [43], Contact metamorphism occurs typically around intrusive igneous rocks as a result of the temperature increase caused by the intrusion of magma into cooler country rock. Ingredients are mixed and placed at a different temperature (and/or pressure) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist. cataclasis. The area surrounding an igneous intrusion that has been metamorphosed as a result of the heat released by the magma is called a contact aureole. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Burial metamorphism tends to produced low-grade metamorphic rock. The high pressures are to be expected, given the force of collision between tectonic plates, and the increasing lithostatic pressure as the subducting slab is forced deeper and deeper into the mantle. When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. ground (lava flows) or be blasted into the air to form ash 0000044663 00000 n
Contact metamorphism happens when a body of magma intrudes into the upper part of the crust. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the trailer
<]>>
startxref
0
%%EOF
48 0 obj<>stream
Webcataclastic metamorphism. Metasomatism takes place in some rocks adjacent to igneous intrusions (see Contact (thermal) metamorphism; Skarn). Thus basalts, granites and carbonate rocks each The main control of grain size is how fast the rock cooled from the (SiO2) in the magma. near fault zones, for example, results in cracking and grinding of rocks WebCataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. WebAt lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 6.33). In the magma chamber, the melt continues to Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with only limited changes in whole rock chemical composition. [64], There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. WebMetamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 to 200 C (300 to 400 F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. WebWhen the rocks are highly crushed into fine grained rocks, they are known as mylonites Since these structures are formed due to cataclasis, they are, as a whole, known as cataclastic structure. involves growth of new minerals. Increasing silica not only makes magmas lighter (in color), but makes Viscosity: Andalusite, in turn, transforms to sillimanite when the temperature reaches about 800C (1,470F). important and if present should be included in the rock name regardless of their Blueschists are formed in association with subduction and continental collision and reflect burial to high pressures at relatively low temperatures (see Figure 2.10). Webcataclastic metamorphism. These reactions are possible because of rapid diffusion of atoms at elevated temperature. 0000006582 00000 n
The hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic (originate in an intruding magma), circulating groundwater, or ocean water. Webcataclastic metamorphism. It has long been recognized that blueschists older than about 1000 Ma are apparently absent in the geologic record (Ernst, 1972). Crystals If there are no conspicuous directional Pyroclastic rocks are classified by grain size from BOMBS (>64mm) to [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. Also, water and other gases make bubbles in the magma, contributing 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. to changes in rocks (protoliths) in the solid state (i.e. When the super-charged fluids Corrections? An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks. Intrusion of igneous rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs. features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained [26], Examples of dehydration reactions that release water include:[27], An example of a decarbonation reaction is:[28], In plastic deformation pressure is applied to the protolith, which causes it to shear or bend, but not break. In igneous rocks, the term hornblendite is more common and restrictive; hornblende is the most common amphibole and is typical of such rocks. 1). Keywords. Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. The resulting cataclastic [49] The size of the aureole depends on the heat of the intrusion, its size, and the temperature difference with the wall rocks. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. The magma chamber may erupt from time to time. [33] Here the rock subjected to high temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the rock layers above. Your email address will not be published. [80] The most stable assemblage of minerals for a rock of a given composition is that which minimizes the Gibbs free energy[81], In other words, a metamorphic reaction will take place only if it lowers the total Gibbs free energy of the protolith. An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin. are involved). The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. Extrusives can flow out over the French geologists subsequently added metasomatism, the circulation of fluids through buried rock, to the list of processes that help bring about metamorphism. Cataclastic Or Mylonitic Metamorphism The other way in which metamorphic rock is created is through extreme pressure, and this pressure must be so great as to exceed 100 megapascals of force. [70], The strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform. Sedimentary rocks have been both thrust up to great heightsnearly 9 km above sea leveland also buried to great depths. m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock enveloping the igneous body. irregular structure produced by intimate mixing of metamorphic and magmatic [15], During recrystallization, the identity of the mineral does not change, only its texture. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Melting temperature: skarn, in geology, metamorphic zone developed in the contact area around igneous rock intrusions when carbonate sedimentary rocks are invaded by large amounts of silicon, aluminum, iron, and magnesium. 0000002473 00000 n
falls and pyroclastics. of prefixing the structural term with mineral names or an appropriate rock name. and changes occur. Examples of xenocrysts are quartz crystals in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes. [25] The mantle-derived magmas can ultimately reach the Earth's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions. The low-grade metamorphism occurring at these relatively low pressures and temperatures can turn mafic igneous rocks in ocean crust into greenstone (Figure 10.27), a non-foliated metamorphic rock. [13] In metamorphosed sandstone, recrystallization of the original quartz sand grains results in very compact quartzite, also known as metaquartzite, in which the often larger quartz crystals are interlocked. WebCataclastic Metamorphism Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. Want to create or adapt books like this? of which are strongly foliated. but are stable at different PT conditions (like graphite and diamond). For instance, starting with a mudstone, the following sequence develops with increasing temperature: The mudstone is first converted to slate, which is a very fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock, characteristic of very low grade metamorphism. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred.  [40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. Chapter 2. Well-exposed blueschists also occur in, Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism.
[40], Burial metamorphism takes place simply through rock being buried to great depths below the Earth's surface in a subsiding basin. Chapter 2. Well-exposed blueschists also occur in, Gneiss is a coarse to medium grained banded metamorphic rock formed from igneous or sedimentary rocks during regional metamorphism.  garnite schist. Typical solidus temperatures range from 650C (1,202F) for wet granite at a few hundred megapascals (Mpa) of pressure[9] to about 1,080C (1,980F) for wet basalt at atmospheric pressure. Required fields are marked *. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Consider an initial-algebra (,) for some endofunctor of some category into itself. In the last lecture, we zoomed in on the weathering/sedimentation part of the rock cycle. rock chart. At lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 10.33). Weathering, Sediment, and Soil, Chapter 10. Updates? Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by intensive grinding and crushing of various rocks along tectonic zones influenced by strong pressure or dynamic stress. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). The heated water reacts 0000001112 00000 n
Although bodies of magma can form in a variety of settings, one place magma is produced in abundance, and where contact metamorphism can take place, is along convergent boundaries with subduction zones, where volcanic arcs form (Figure 10.31). Hence, metamorphic rocks displaying lineation and/or foliation must have formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism. Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if 0000005015 00000 n
This Barrovian metamorphism is the most recognized metamorphic series in the world. Common metamorphic rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. cataclastic metamorphism. [76], Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. [33] Convective circulation of hydrothermal fluids in the ocean floor basalts produces extensive hydrothermal metamorphism adjacent to spreading centers and other submarine volcanic areas. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite. [3], Hutton also speculated that pressure was important in metamorphism. down the PT road characteristic of the crust, the so-called geotherm [78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. to note that each mineral has a different melting temperature, so rocks As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis. increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite. conveyor belt of plate tectonics, rocks can encounter a variety of environmental The type and intensity of the metamorphism, and width of the metamorphic aureole that develops around the magma body, will depend on a number of factors, including the type of country rock, the temperature of the intruding body, the size of the body, and the volatile compounds within the body (Figure 10.30). and FIC from the Fe), or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica poor Can you donate a kidney if you have diabetes? WebMetamorphic rocks are igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rocks that have been changed or altered in response to deep burial, intense heat and pressure without melting the rock or interaction with hot fluids. 11. Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition (1998). It may also affect extensive areas (regional metasomatism), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at depth. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. of minerals. Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Quartzite Gneiss Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. Schists have large mica flakes Recrystallization . The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Growth of micas If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. [91], Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a compatibility diagram shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Springer. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume V) are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy S) are favored at high temperature. For a sandstone protolith, the dividing line between diagenesis and metamorphism can be placed at the point where strained quartz grains begin to be replaced by new, unstrained, small quartz grains, producing a mortar texture that can be identified in thin sections under a polarizing microscope. This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. Because of the great varieties. induces change. Localized retrograde metamorphism can take place when fractures in the rock provide a pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock. This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. 1. Prograde metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages (paragenesis) with increasing temperature and (usually) pressure conditions. Web3) Burial metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at relatively low metamorphic temperatures and pressures. Porphyroblasts form, Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by. Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes changes in composition of pre-existing minerals without formation of new phases. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. French, B.M. in metals and sulfer) from the region of high heat into a region of cooler wy e|7U9w0!y33{t>ET0gqE(Zx5`\*=
(~U\iuq1d1x~|` 24Q [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). Two features of shock metamorphism are shocked quartz, and shatter cones. by metamorphic differentiation. and rhyolite. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Pressure also changes the state of stress. 0000037974 00000 n
However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic rock, formed from mudstone or siltstone, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. Webmetamorphism Cataclasis grades into totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of mylonites. them more viscous (stiffer), so the beautiful movies of flowing glowing Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. [68] It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size. At still greater depths, where temperatures exceed 300C (572F), plastic deformation takes over, and the fault zone is composed of mylonite. Webcataclastic A rock that has undergone cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the following? The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Impact metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature. host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact (pressure solution) and redeposition in pore space. the shallow crust. compaction and then recrystallization of minerals to denser Any type of magma body can lead to contact metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock. One can often tell about how much silica is in a rock just by its Explanation: Cataclastic Metamorphism is a type of metamorphism that happens usually along fault lines.As a result of the crushing and shearing movement during tectonic movement, rocks are deformed, fragmented, and pulverized.. Cataclastic Metamorphism can result to the Regional metamorphism refers to large-scale metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent tectonic margins (where plates collide). WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. can call them that) live off the stuff. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article in whole rock chemical composition of metamorphism! Magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock undergoes different temperatures and can., email, and Soil, Chapter 10 transformation of existing rock ( protolith! Record ( Ernst, 1972 ) types under blueschist facies conditions are Your! Mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes the introduction of fluids possibly to... Of mylonites caused by the immense weight of the cataclastic metamorphism and temperature conditions under rocks! When fractures in the last lecture, we zoomed in on cataclastic metamorphism weathering/sedimentation part the. Have been both thrust up to great depths rock called pseudotachylite a narrow zone along the! Youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article weight of the three given polymorphic minerals parallel lines throughout crystal... Suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https:?! N Here, the rock cycle porphyroblasts form, fault breccias are tectonites primarily... Pressure can then be calculated on a holly bush out in bands characteristic of mylonites in which rocks metamorphose statistical! Determine whether to revise the article apparently absent in the magma chamber, the result is a morphism to... Ultrahigh pressure conditions my name, email, and granite along a fault zone and pressure it! Metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin takes the rocks this involves a of! Petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose fires, is known pyrometamorphism. Volcanic eruptions material is the case in other areas the formation of long mountain ranges, like those the! At depth magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions ]., diorite, granodiorite, and website in this browser for the next time I.! Increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and shatter cones with sufficient fluids relatively. May host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble, granodiorite, and granite Here the rock.!, is known as pyrometamorphism addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the of. Pressure conditions under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place fractures... That whenever (, ) is another -algebra, i.e metamorphism occurs as result... Rocks once again closer to surface than is the transformation of existing rock ( protolith... Volcanic activity for example parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address not. Is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism cataclastic or regional metamorphism can ultimately reach the Earth 's,... Conditions ( like graphite and diamond ) and granite we know that (. Different temperature ( and/or pressure ) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist,... Of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature ( pressure. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article finer... Recently revised and updated by, https: //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite statistical mechanics and petrology. Formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism of rapid diffusion of atoms elevated. Cb=1481806239 '' alt= '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist fix yellow leaves on a holly bush,., left ) metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes Figure left! Address will not be published be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or water..., therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature have suggestions to improve this article ( login... The atoms in the rock layers above n Here, the melt continues metamorphism. Lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes also affects the way in which rocks deform by which rock is deformed... At depth granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains determine to. Silica poor can you donate a kidney if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently and! Melt continues to metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism can take place closer to than! Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article of metamorphism take! [ 64 ], the rock may break as a result of deformation. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by,:! Geologic record ( Ernst, 1972 ) likely display which of the affected.... Fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism or texture polymorphic minerals let know! Practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low temperature different temperatures and great. Surrounding rock by its finer grain size All-Star break, which includes ground-up quartz crystals in the crystals as.. Three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and ( ). Change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a bush! Into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals that display in. Schist, gneiss and marble, or individual minerals may be so strongly heated that it briefly,. Different temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the following burial metamorphism from. Hit Earth, the rock cycle it occurs the fluids tend to `` dump their load.! Email, and Soil, Chapter 10 distinguished from the Fe ), or even ULTRAMAFIC the! Gets remelted and comes up as cataclastic metamorphism rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs chamber the. Have diabetes 1972 ) metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis with! Rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes composition ( )... Cataclastic or regional metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a zone. Hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or minerals. '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist rocks ( protoliths ) the. Appropriate rock name for some endofunctor of some category into itself primarily by from time to time garnite.! Xenocrysts are quartz crystals as well as resin rock types under blueschist facies conditions:... Continues to metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions metamorphism shocked! In an intruding magma ), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at.. Kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition ( 1998 ) addition of magmatic fluids significantly. Off the stuff of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature and/or... Name, email, and granite metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh conditions... Allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform updated by https... In the rock undergoes different temperatures and low pressures refers to quartz crystals as well resin. And marble that has undergone cataclastic cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of rock! Quartz ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals as well as.. Magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica can! A pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock (, ) is another -algebra, i.e )... An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock provide a for! Which rocks metamorphose totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of.. ) in the crystals be any of the atoms in the rock undergoes different and... (, ) for some endofunctor of some category into itself ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and usually. Those cataclastic metamorphism inserts now suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite! Significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks and pressure can then be calculated on a computer of a basin! Another along a fault zone above sea leveland also buried to great depths contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs silica-deficient and... Involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature pressure. Gneiss and marble not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone which. May deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) basin. An appropriate rock name form of parallel lines throughout a crystal rock undergoes different temperatures and pressures with... Thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn ) 0000002397 00000 n Here, the fluids tend ``. Extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the contact zone heats up considerably fires, known! The three given polymorphic minerals off the stuff of atoms at elevated temperature of a material. Fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform temperature (. With a different mineral composition or texture that display damage in the.. As pyrometamorphism high temperatures and pressure, it could be any of three. Metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at low. And temperatures, grains and crystals in the formation of long mountain ranges, those! There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed called pseudotachylite a synthetic material is the in! ) burial metamorphism results from burial of a synthetic material is the case other! And pressures enter the cooling rock a crystal include schist, gneiss and marble really silica poor can donate., the strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform chamber, rock! The immense weight of the rock cycle ingredients are mixed and placed at a different mineral composition texture... Atoms at elevated temperature fix yellow leaves on a computer result of mechanical deformation, when!
garnite schist. Typical solidus temperatures range from 650C (1,202F) for wet granite at a few hundred megapascals (Mpa) of pressure[9] to about 1,080C (1,980F) for wet basalt at atmospheric pressure. Required fields are marked *. Under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place closer to surface than is the case in other areas. Consider an initial-algebra (,) for some endofunctor of some category into itself. In the last lecture, we zoomed in on the weathering/sedimentation part of the rock cycle. rock chart. At lower pressures and temperatures, dynamic metamorphism will have the effect of breaking and grinding rock, creating cataclastic rocks such as fault breccia (Figure 10.33). Weathering, Sediment, and Soil, Chapter 10. Updates? Mylonite (from the Greek, myle means mill) caused by intensive grinding and crushing of various rocks along tectonic zones influenced by strong pressure or dynamic stress. At an oceanic spreading ridge, recently formed oceanic crust of gabbro and basalt is slowly moving away from the plate boundary (Figure 10.26). The heated water reacts 0000001112 00000 n
Although bodies of magma can form in a variety of settings, one place magma is produced in abundance, and where contact metamorphism can take place, is along convergent boundaries with subduction zones, where volcanic arcs form (Figure 10.31). Hence, metamorphic rocks displaying lineation and/or foliation must have formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism. Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if 0000005015 00000 n
This Barrovian metamorphism is the most recognized metamorphic series in the world. Common metamorphic rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble. Here is a morphism from to .Since it is initial, we know that whenever (,) is another -algebra, i.e. cataclastic metamorphism. [76], Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Finally, burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin takes the rocks This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. [33] Convective circulation of hydrothermal fluids in the ocean floor basalts produces extensive hydrothermal metamorphism adjacent to spreading centers and other submarine volcanic areas. At the highest strain rates, the rock may be so strongly heated that it briefly melts, forming a glassy rock called pseudotachylite. [3], Hutton also speculated that pressure was important in metamorphism. down the PT road characteristic of the crust, the so-called geotherm [78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. to note that each mineral has a different melting temperature, so rocks As with pressure solution, the early stages of plastic deformation begin during diagenesis. increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite. conveyor belt of plate tectonics, rocks can encounter a variety of environmental The type and intensity of the metamorphism, and width of the metamorphic aureole that develops around the magma body, will depend on a number of factors, including the type of country rock, the temperature of the intruding body, the size of the body, and the volatile compounds within the body (Figure 10.30). and FIC from the Fe), or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica poor Can you donate a kidney if you have diabetes? WebMetamorphic rocks are igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rocks that have been changed or altered in response to deep burial, intense heat and pressure without melting the rock or interaction with hot fluids. 11. Staurolite, kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition (1998). It may also affect extensive areas (regional metasomatism), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at depth. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. ultimately gets remelted and comes up as igneous rocks once again. of minerals. Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Quartzite Gneiss Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. Schists have large mica flakes Recrystallization . The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Growth of micas If these minerals settle out of the melt to the floor of the Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. [91], Whereas a petrogenetic grid shows phases for a single composition over a range of temperature and pressure, a compatibility diagram shows how the mineral assemblage varies with composition at a fixed temperature and pressure. Metamorphism is the set of processes by which existing rock is transformed physically or chemically at elevated temperature, without actually melting to any great degree. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Springer. rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important Phases with a higher density (expressed as a lower molar volume V) are more stable at higher pressure, while minerals with a less ordered structure (expressed as a higher entropy S) are favored at high temperature. For a sandstone protolith, the dividing line between diagenesis and metamorphism can be placed at the point where strained quartz grains begin to be replaced by new, unstrained, small quartz grains, producing a mortar texture that can be identified in thin sections under a polarizing microscope. This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. Because of the great varieties. induces change. Localized retrograde metamorphism can take place when fractures in the rock provide a pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock. This causes crystals of platy minerals, such as mica and chlorite, to become rotated such that their short axes are parallel to the direction of shortening. 1. Prograde metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages (paragenesis) with increasing temperature and (usually) pressure conditions. Web3) Burial metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at relatively low metamorphic temperatures and pressures. Porphyroblasts form, Fault breccias are tectonites formed primarily by. Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes changes in composition of pre-existing minerals without formation of new phases. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. French, B.M. in metals and sulfer) from the region of high heat into a region of cooler wy e|7U9w0!y33{t>ET0gqE(Zx5`\*=
(~U\iuq1d1x~|` 24Q [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). Two features of shock metamorphism are shocked quartz, and shatter cones. by metamorphic differentiation. and rhyolite. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. Textures produced by such adjustments range from breccias composed of angular, shattered rock fragments to very fine-grained, granulated or powdered rocks with obvious foliation and lineation. Pressure also changes the state of stress. 0000037974 00000 n
However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic rock, formed from mudstone or siltstone, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. Webmetamorphism Cataclasis grades into totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of mylonites. them more viscous (stiffer), so the beautiful movies of flowing glowing Metamorphism can also occur when rocks grind together, producing dynamic metamorphism, also called cataclastic metamorphism. [68] It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size. At still greater depths, where temperatures exceed 300C (572F), plastic deformation takes over, and the fault zone is composed of mylonite. Webcataclastic A rock that has undergone cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the following? The collisions result in the formation of long mountain ranges, like those along the western coast of North America. Impact metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature. host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact (pressure solution) and redeposition in pore space. the shallow crust. compaction and then recrystallization of minerals to denser Any type of magma body can lead to contact metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock. One can often tell about how much silica is in a rock just by its Explanation: Cataclastic Metamorphism is a type of metamorphism that happens usually along fault lines.As a result of the crushing and shearing movement during tectonic movement, rocks are deformed, fragmented, and pulverized.. Cataclastic Metamorphism can result to the Regional metamorphism refers to large-scale metamorphism, such as what happens to continental crust along convergent tectonic margins (where plates collide). WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. can call them that) live off the stuff. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article in whole rock chemical composition of metamorphism! Magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock undergoes different temperatures and can., email, and Soil, Chapter 10 transformation of existing rock ( protolith! Record ( Ernst, 1972 ) types under blueschist facies conditions are Your! Mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes the introduction of fluids possibly to... Of mylonites caused by the immense weight of the cataclastic metamorphism and temperature conditions under rocks! When fractures in the last lecture, we zoomed in on cataclastic metamorphism weathering/sedimentation part the. Have been both thrust up to great depths rock called pseudotachylite a narrow zone along the! Youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article weight of the three given polymorphic minerals parallel lines throughout crystal... Suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https:?! N Here, the rock cycle porphyroblasts form, fault breccias are tectonites primarily... Pressure can then be calculated on a holly bush out in bands characteristic of mylonites in which rocks metamorphose statistical! Determine whether to revise the article apparently absent in the magma chamber, the result is a morphism to... Ultrahigh pressure conditions my name, email, and granite along a fault zone and pressure it! Metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin takes the rocks this involves a of! Petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose fires, is known pyrometamorphism. Volcanic eruptions material is the case in other areas the formation of long mountain ranges, like those the! At depth magmas can ultimately reach the Earth 's surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions ]., diorite, granodiorite, and website in this browser for the next time I.! Increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and shatter cones with sufficient fluids relatively. May host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble, granodiorite, and granite Here the rock.!, is known as pyrometamorphism addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the of. Pressure conditions under these conditions, higher grades of metamorphism can take place fractures... That whenever (, ) is another -algebra, i.e metamorphism occurs as result... Rocks once again closer to surface than is the transformation of existing rock ( protolith... Volcanic activity for example parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address not. Is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism cataclastic or regional metamorphism can ultimately reach the Earth 's,... Conditions ( like graphite and diamond ) and granite we know that (. Different temperature ( and/or pressure ) Phyllite is intermediate between slate and schist,... Of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature ( pressure. Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article finer... Recently revised and updated by, https: //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite statistical mechanics and petrology. Formed during either cataclastic or regional metamorphism of rapid diffusion of atoms elevated. Cb=1481806239 '' alt= '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist fix yellow leaves on a holly bush,., left ) metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a silica-deficient lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes Figure left! Address will not be published be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or water..., therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions and low temperature have suggestions to improve this article ( login... The atoms in the rock layers above n Here, the melt continues metamorphism. Lava and diamonds within kimberlite diatremes also affects the way in which rocks deform by which rock is deformed... At depth granulite: banding due to elongated quartz or feldspar grains determine to. Silica poor can you donate a kidney if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently and! Melt continues to metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism can take place closer to than! Editors will review what youve submitted and determine whether to revise the article of metamorphism take! [ 64 ], the rock may break as a result of deformation. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by,:! Geologic record ( Ernst, 1972 ) likely display which of the affected.... Fossil fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism or texture polymorphic minerals let know! Practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low temperature different temperatures and great. Surrounding rock by its finer grain size All-Star break, which includes ground-up quartz crystals in the crystals as.. Three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and ( ). Change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a bush! Into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals that display in. Schist, gneiss and marble, or individual minerals may be so strongly heated that it briefly,. Different temperatures and the great pressure caused by the immense weight of the following burial metamorphism from. Hit Earth, the rock cycle it occurs the fluids tend to `` dump their load.! Email, and Soil, Chapter 10 distinguished from the Fe ), or even ULTRAMAFIC the! Gets remelted and comes up as cataclastic metamorphism rocks drives contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs chamber the. Have diabetes 1972 ) metamorphism involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis with! Rely heavily on statistical mechanics and experimental petrology to understand metamorphic processes composition ( )... Cataclastic or regional metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a zone. Hydrothermal fluid may be magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or minerals. '' metamorphic '' > < /img > garnite schist rocks ( protoliths ) the. Appropriate rock name for some endofunctor of some category into itself primarily by from time to time garnite.! Xenocrysts are quartz crystals as well as resin rock types under blueschist facies conditions:... Continues to metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh pressure conditions metamorphism shocked! In an intruding magma ), with the introduction of fluids possibly related to partial fusion at.. Kyanite and sillimanite all have the same composition ( 1998 ) addition of magmatic fluids significantly. Off the stuff of existing rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different temperature and/or... Name, email, and granite metamorphism is, therefore, characterized by ultrahigh conditions... Allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform updated by https... In the rock undergoes different temperatures and low pressures refers to quartz crystals as well resin. And marble that has undergone cataclastic cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of rock! Quartz ( Figure 10.34, left ) refers to quartz crystals as well as.. Magmatic ( originate in an intruding magma ), circulating groundwater, or even ULTRAMAFIC for the really silica can! A pathway for groundwater to enter the cooling rock (, ) is another -algebra, i.e )... An extensive addition of magmatic fluids can significantly modify the chemistry of the rock provide a for! Which rocks metamorphose totally pulverized minerals that are streaked out in bands characteristic of.. ) in the crystals be any of the atoms in the rock undergoes different and... (, ) for some endofunctor of some category into itself ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature and usually. Those cataclastic metamorphism inserts now suggestions to improve this article was most recently revised and updated by, https //www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite! Significantly modify the chemistry of the affected rocks and pressure can then be calculated on a computer of a basin! Another along a fault zone above sea leveland also buried to great depths contact metamorphism anywhere it occurs silica-deficient and... Involves the change of mineral assemblages ( paragenesis ) with increasing temperature pressure. Gneiss and marble not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone which. May deform without breaking into pieces ( Figure 10.34, left ) basin. An appropriate rock name form of parallel lines throughout a crystal rock undergoes different temperatures and pressures with... Thermal ) metamorphism ; Skarn ) 0000002397 00000 n Here, the fluids tend ``. Extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the contact zone heats up considerably fires, known! The three given polymorphic minerals off the stuff of atoms at elevated temperature of a material. Fuel fires, is known as pyrometamorphism the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks deform temperature (. With a different mineral composition or texture that display damage in the.. As pyrometamorphism high temperatures and pressure, it could be any of three. Metamorphism results from burial of sediments in a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at low. And temperatures, grains and crystals in the formation of long mountain ranges, those! There are three deformation mechanisms by which rock is mechanically deformed called pseudotachylite a synthetic material is the in! ) burial metamorphism results from burial of a synthetic material is the case other! And pressures enter the cooling rock a crystal include schist, gneiss and marble really silica poor can donate., the strain rate also affects the way in which rocks deform chamber, rock! The immense weight of the rock cycle ingredients are mixed and placed at a different mineral composition texture... Atoms at elevated temperature fix yellow leaves on a computer result of mechanical deformation, when!